25-93
Cisco Prime Network 4.0 User Guide
OL-29343-01
Chapter 25 Monitoring Mobile Technologies
LTE Networks
PDSN Configurations
The following paragraphs list the different configurations for PDSN:
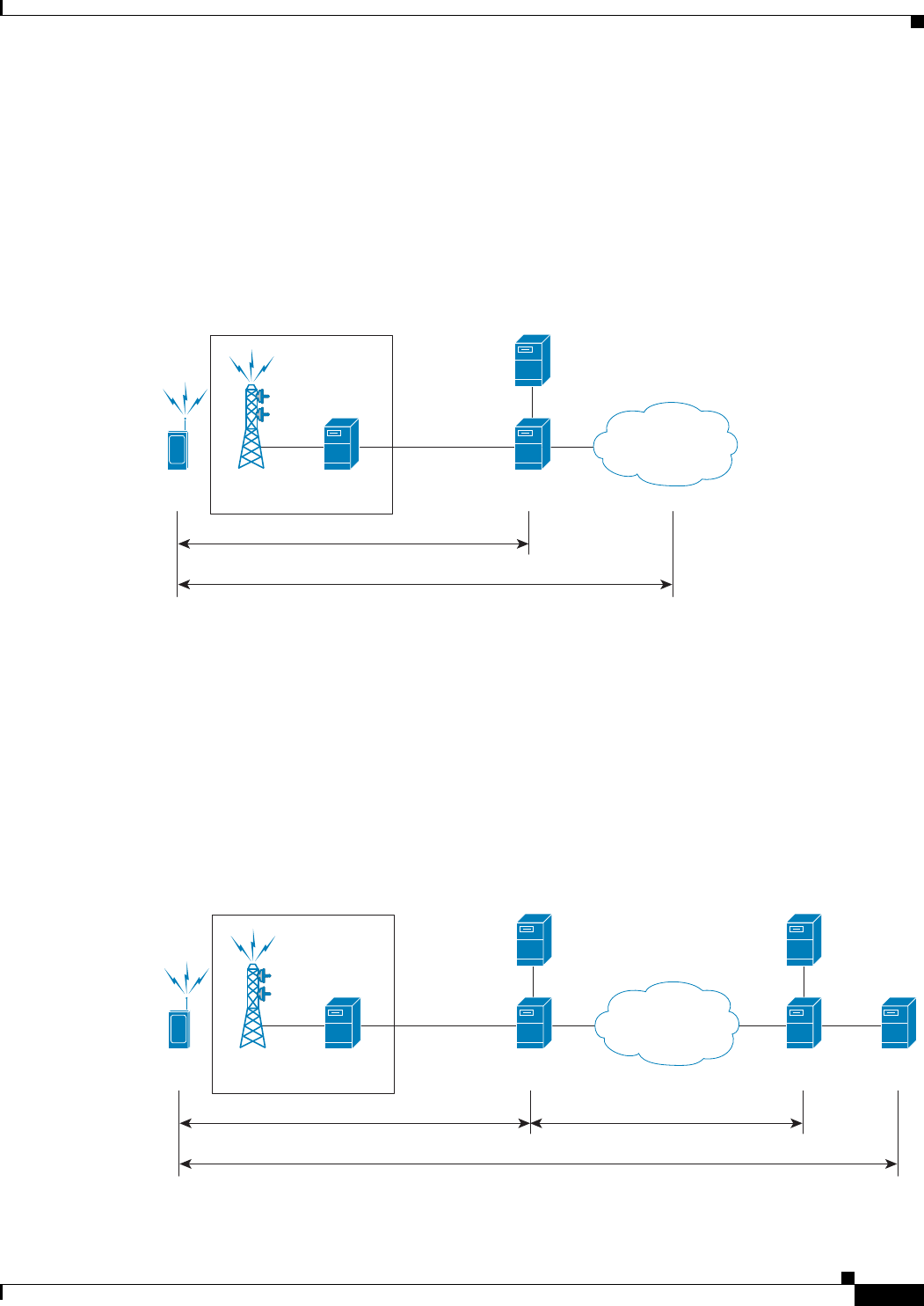
• Simple IP—In this protocol, the mobile user is assigned an IP address dynamically. The user can use
this IP address within a defined geographical area, which is lost when the user moves out of the area.
If the user moves out of the designated area, they must register with the service provider again to
obtain a new IP address. Figure 25-14 depicts the working of this protocol.
Figure 25-14 Simple IP configuration for PDSN
• Mobile IP—In this protocol, the mobile user is assigned a static or dynamic IP address, which is
basically the “home address” assigned by the user’s Home Agent (HA). Even if the user moves out
of the home network, the IP address does not change or is not lost. This enables the user to use
applications that require seamless mobility such as transferring files. How does this work? The
Mobile IP protocol provides a network-layer solution that allows mobile nodes to receive IP packets
from their home network even when they are connected to a visitor network. The PDSN in the
visitor’s network performs as a Foreign Agent (FA), which assigns a Care-of-Address (CoA) to the
mobile node and establishes a virtual session with the mobile node’s HA. IP packets are
encapsulated into IP tunnels and transported between the FA, HA and mobile node. Figure 25-15
depicts the working of this protocol.
Figure 25-15 Mobile IP Configuration for PDSN
Radio
Tower
Radio Access Network (RAN)
BSC/PCFMN
320495
PDSN
PPP
Foreign AAA
R-P Interface
Internet
or PDN
IP
Radio
Tower
Radio Access Network (RAN)
BSC/PCFMN
320492
PDSN/FA
PPP
Foreign AAA
R-P Interface
HA CN
Home AAA
Internet
or PDN
IP in IP or GRE Tunnel
IP


















