11-3
Cisco Prime Network 4.0 User Guide
OL-29343-01
Chapter 11 Using Cisco PathTracer to Diagnose Problems
Launching Path Tracer
In MPLS and Carrier Ethernet environments, Cisco PathTracer can trace paths across:
• Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) configurations—A path trace along a CSC flow follows the path
from the customer CE through the customer carrier VPN, across the customer backbone carrier
VPN, back to the customer carrier VPN, and to the destination CE.
• VLANs—A path trace across VLANs follows the path based on the forwarding table, which means
that the trace follows ports in the Forwarding STP state.
• Q-in-Q—A path trace across Q-in-Q creates a single path trace (if the MAC address is learned) or a
multiple-path (multipath) trace if the MAC address is not in the forwarding table. If the VLAN
bridge has not learned a given MAC address, the bridge floods the Ethernet frame to the confines of
a given VLAN or switching entity and across those ports that allow the given VLAN identifier. A
MAC/VLAN path trace can be conducted from a customer edge (CE) VLAN interface across a
service provider (SP) VLAN; that is, across Q-in-Q configurations with the CE-VLAN identifier as
the inner VLAN identifier and Cisco PathTracer detecting the outer SP-VLAN identifier that
encapsulates the CE-VLAN.
• Pseudowires (also known as EoMPLS)—A MAC/VLAN path trace can be conducted from a VLAN
interface across a VLAN attachment to a pseudowire.
• VLAN-VPLS-VLAN configurations—A multiple-point MAC/VLAN path trace can be conducted
on CE-VLANs across a service provider VPLS transport from a VLAN interface that attaches to the
VPLS.
In addition, Cisco PathTracer can trace a path:
• If the destination MAC address is not reachable—If Cisco PathTracer cannot complete a
MAC/VLAN path trace to a specified destination MAC address across an MPLS core, VPLS, or
H-VPLS, then Cisco PathTracer displays the portion of the path that Cisco PathTracer can trace
toward the destination MAC address.
• That contains a simulated Ethernet frame—Cisco PathTracer can trace a simulated Ethernet frame
from a VLAN port, across a VLAN (VLAN-based flow domain fragment), VPLS (VPLS-based flow
domain fragment), and VLAN, for an end-to-end MAC address trace.
Prime Network derives the various paths on the network from its up-to-date knowledge of the network.
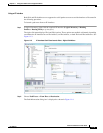
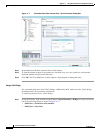
After a user selects a source and destination, Cisco PathTracer finds and retrieves the path of a specified
service, and displays the path in the Cisco PathTracer window. The retrieved information contains
network elements in the path, including all properties at Layer 1, Layer 2, and Layer 3, plus alarm
information, counters, and more, all of which is available via Cisco PathTracer.
Launching Path Tracer
Cisco PathTracer can be launched from a bridge, switching entity, Ethernet interface, Ethernet flow
point, VLAN interface, ATM VC, DLCI, or IP interface entry point. Ethernet flow points can be starting
points whether they are associated with an interface, bridge, or LAG.
The virtual route is found according to the cross connect table of each ATM switch or Frame Relay
device. The IP routing and path-finding process is enabled according to the VRF tables of each router,
and the Ethernet-simulated path is found according to the various Layer 2 forwarding tables, such as
bridges or VSIs.