20-36
Cisco Prime Network 4.0 User Guide
OL-29343-01
Chapter 20 Monitoring MToP Services
Network Clock Service Overview
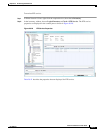
Monitoring PTP Service
In networks that employ TDM, periodic synchronization of device clocks is required to ensure that the
receiving device knows which channel is which for accurate reassembly of the data stream. The
Precision Time Protocol (PTP) standard:
• Specifies a clock synchronization protocol that enables this synchronization.
• Applies to distributed systems that consist of one or more nodes communicating over a network.
Defined by IEEE 1588-2008, PTP Version 2 (PTPv2) allows device synchronization at the nanosecond
level.
PTP uses the concept of master and slave devices to achieve precise clock synchronization. Using PTP,
the master device periodically starts a message exchange with the slave devices. After noting the times
at which the messages are sent and received, each slave device calculates the difference between its
system time and the system time of the master device. The slave device then adjusts its clock so that it
is synchronized with the master device. When the master device initiates the next message exchange, the
slave device again calculates the difference and adjusts its clock. This repetitive synchronization ensures
that device clocks are coordinated and that data stream reassembly is accurate. For configuring PTP, see
Configuring SONET, page 20-53.
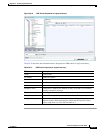
Use Stratum4 Quality of the clock source:
• True—Use Stratum 4, the lowest level of clocking quality.
• False—(Default) Use Stratum 3, a higher level of clocking quality than
Stratum 4.
Clock Source Table
This table is displayed only if there are active clock sources.
Clock Source Current active clock source used by the device.
Network Clock
Priority
Priority of the clock source with 1 being the highest priority.
Source Type Method by which clocking information is provided:
• BITS—Timing is supplied by a Building Integrated Timing Supply (BITS)
port clock.
• E1/T1—Clocking is provided via an E1 or T1 interface.
• Packet-Timing—Clocking is provided over a packet-based network.
• Synchronous Ethernet—Clocking is provided by Synchronous Ethernet.
• Others—Clocking is provided by a source other than the above.
Valid Source Validity of the clock source:
• True—The clock source is valid and operational.
• False—The clock source is not valid or is not operational.
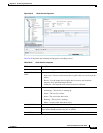
Table 20-20 Clock Service Properties (continued)
Field Description