Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com.
29-13
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide
OL-6965-03, Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.x
Chapter 29 IPsec and IKE
Modifying IKE and IPsec
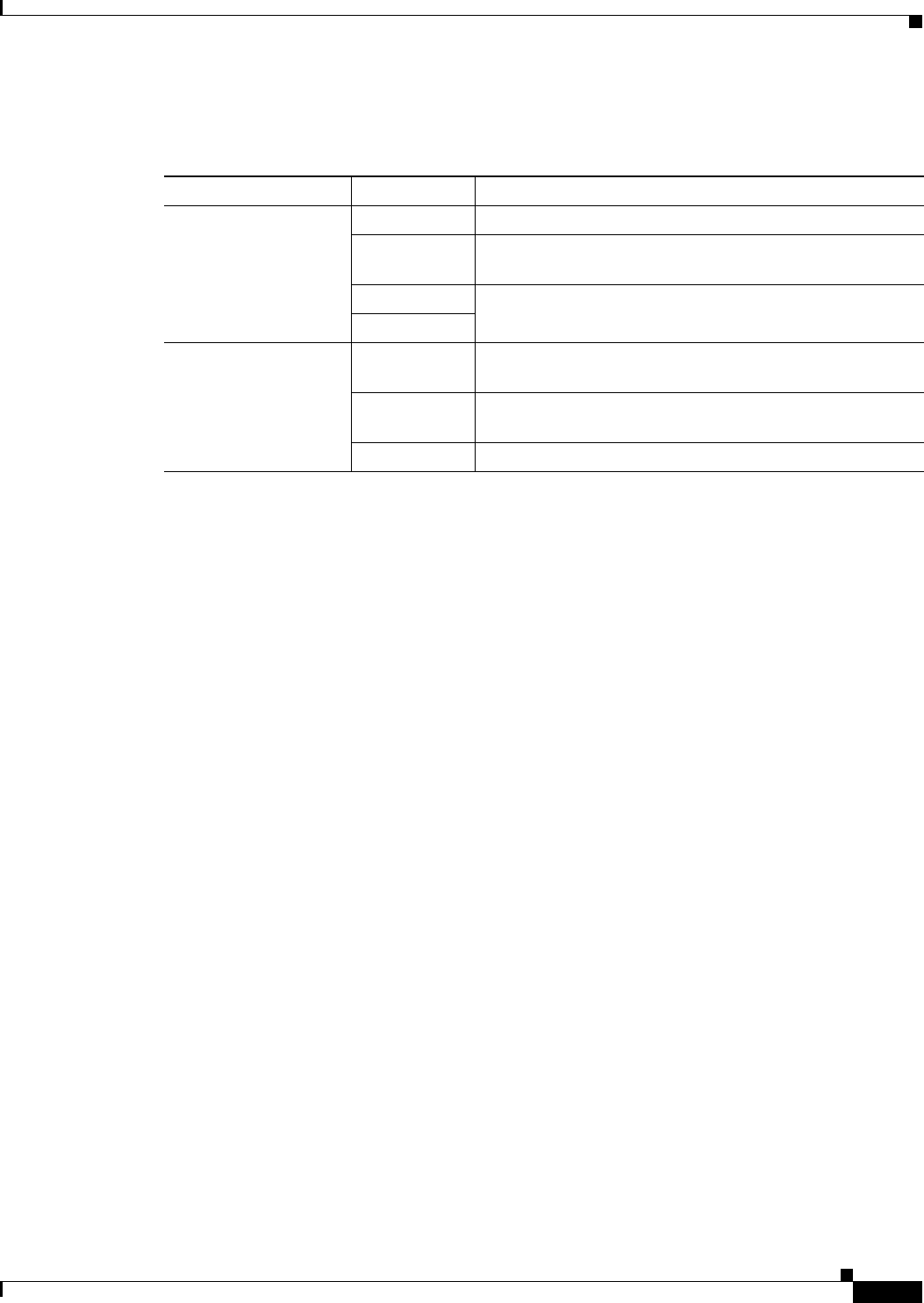
Table 29-2 provides a list of allowed transform combinations.
Crypto Map Entries
Once you have created the crypto ACLs, you can create crypto map sets to the interfaces. Crypto map
IPsec entries pull together the various parts of the IPsec SA, including:
• The traffic to be protected by IPsec (per the crypto ACL). A crypto map set can contain multiple
entries, each with a different ACL.
• The granularity of the flow to be protected by a set of SAs.
• The IPsec-protected traffic destination (who the remote IPsec peer is).
• The local address to be used for the IPsec traffic (applying to an interface).
• The IPsec security to be applied to this traffic (selecting from a list of one or more transform sets)
• Other parameters to define an IPsec SA
Crypto map entries with the same crypto map name (but different map sequence numbers) are grouped
into a crypto map set.
When you apply a crypto map set to an interface, the following events occur:
• A security policy database (SPD) is created for that interface
• All IP traffic passing through the interface is evaluated against the SPD.
If a crypto map entry sees outbound IP traffic that requires protection, an SA is negotiated with the
remote peer according to the parameters included in the crypto map entry.
The policy derived from the crypto map entries is used during the negotiation of SAs. If the local switch
initiates the negotiation, it will use the policy specified in the crypto map entries to create the offer to be
sent to the specified IPsec peer. If the IPsec peer initiates the negotiation, the local switch checks the
policy from the crypto map entries and decide whether to accept or reject the peer's request (offer).
For IPsec to succeed between two IPsec peers, both peers' crypto map entries must contain compatible
configuration statements.
Table 29-2 Allowed Transform Combinations
Transform Type Transform Description
ESP encryption
1
transform (pick one.)
1. Mandatory.
esp-des ESP with the 56-bit DES encryption algorithm
esp-3des ESP with the 168-bit DES encryption algorithm (3DES or
Triple DES)
aes-128 In both counter mode
2
and CBC
2. If you select counter mode ESP encryption, authentication is required.
aes-256
ESP authentication
3
transform (pick one.)
3. Optional in all other encryption cases (except counter mode).
esp-md5-hmac ESP with the MD5 (HMAC variant) authentication
algorithm
esp-sha-hmac ESP with the SHA (HMAC variant) authentication
algorithm
aes-xcbc-mac AES SCBC (MAC variant) ESP authentication algorithm


















