Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com.
18-2
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide
OL-6965-03, Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.x
Chapter 18 Interface Configuration
Fibre Channel Interfaces
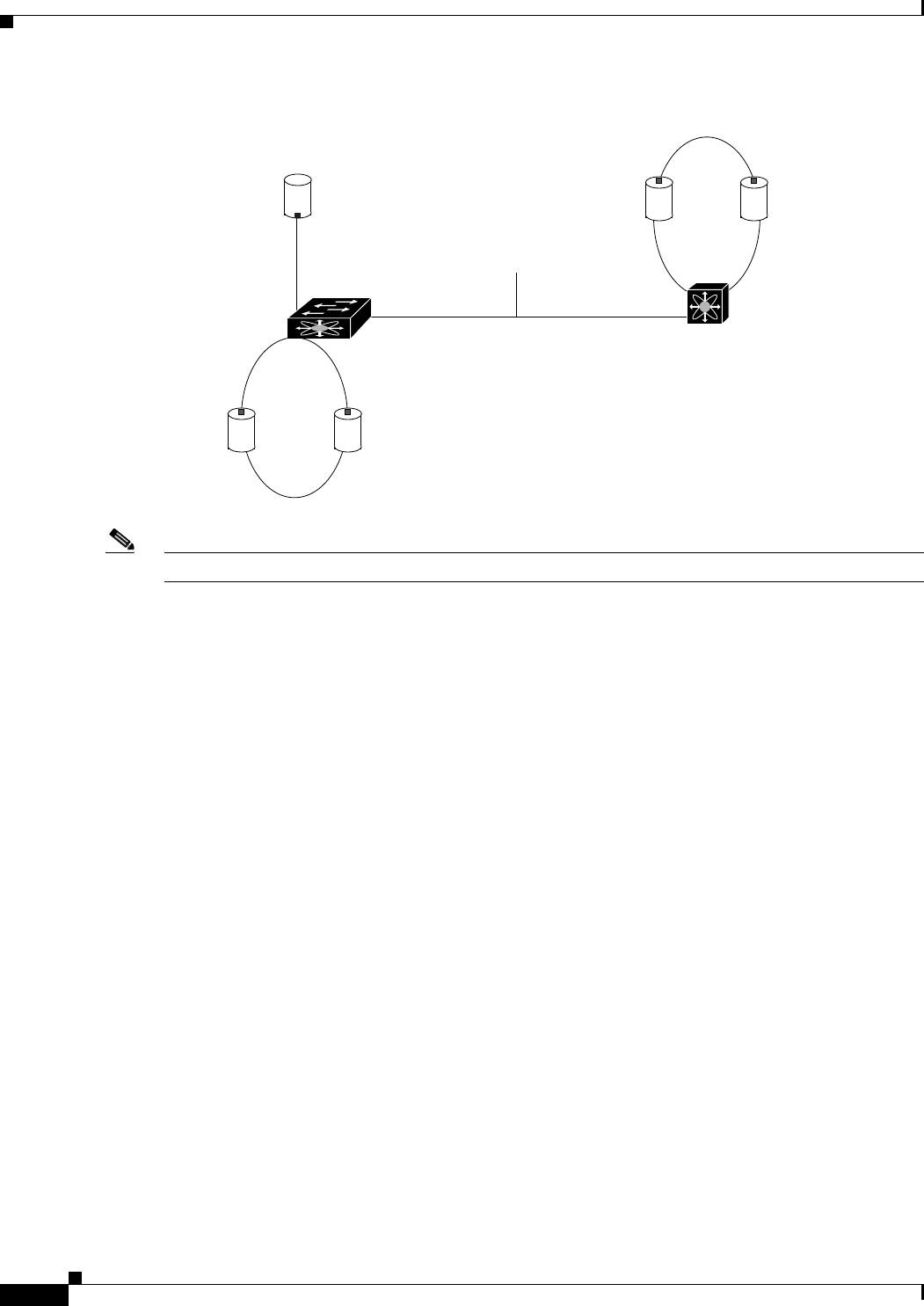
Figure 18-1 Cisco MDS 9000 Family Switch Interface Modes
Note Interfaces are created in VSAN 1 by default. See Chapter 13, “VSAN Configuration.”
Each interface has an associated administrative configuration and an operational status:
• The administrative configuration does not change unless you modify it. This configuration has
various attributes that you can configure in administrative mode.
• The operational status represents the current status of a specified attribute like the interface speed.
This status cannot be changed and is read-only. Some values may not be valid when the interface is
down (for example, the operational speed).
A brief description of each interface mode follows.
E Port
In expansion port (E port) mode, an interface functions as a fabric expansion port. This port may be
connected to another E port to create an Inter-Switch Link (ISL) between two switches. E ports carry
frames between switches for configuration and fabric management. They serve as a conduit between
switches for frames destined to remote N ports and NL ports. E ports support class 2, class 3, and class
F service.
An E port connected to another switch may also be configured to form a PortChannel (see Chapter 17,
“PortChannel Configuration”).
F Port
In fabric port (F port) mode, an interface functions as a fabric port. This port may be connected to a
peripheral device (host or disk) operating as an N port. An F port can be attached to only one N port. F
ports support class 2 and class 3 service.
N port
F port
Public
loop
loop
E port E port
FL port
NL port NL port
NL port NL port
p
FL port
ISL link
79528
Public


















