776
FX3G/FX3U/FX3UC Series Programmable Controllers
Programming Manual - Basic & Applied Instruction Edition
35 SFC Program and Step Ladder
35.1 SFC Program
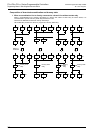
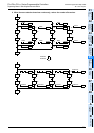
Examples of flows having selective branches and recombination
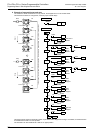
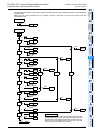
1. Operation of selective branch
• When two or more flows are provided and
either one is selected and executed, it is
called a selective branch.
• In the example shown on the right, X000,
X010 and X020 should not turn ON at the
same time.
• For example, when X000 turns ON while
S20 is ON, the ON status is transferred to
S21; S20 turns OFF, and S21 turns ON.
Accordingly, even if X010 or X020 turns
ON after that, S31 and S41 do not turn ON.
• The recombination state relay S50 is
driven by either one among S22, S32 and
S42.
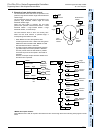
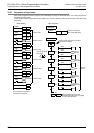
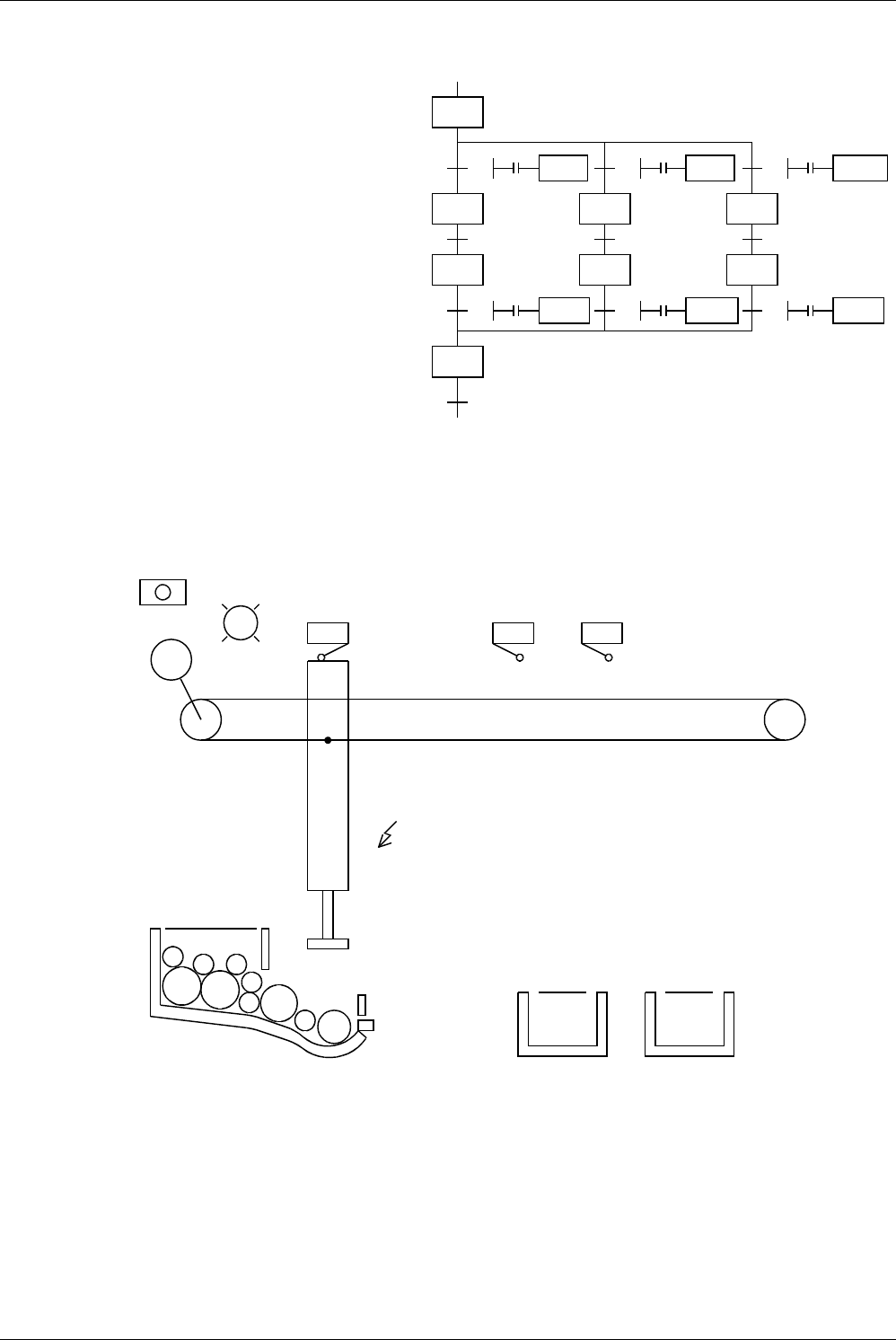
2. Example of selecting and carrying large and small balls
The figure below shows a mechanism which selects and carries large and small balls using conveyors.
The upper left position is regarded as the origin, and the mechanism performs in the order “moving down → suction →
moving up → moving rightward → moving down → release → moving up → moving leftward”.
When the arm moves down and the electromagnet pushes a large ball, the lower limit switch LS2 turns OFF. When
the electromagnet pushes a small ball, LS2 turns ON.
20
1
21
2
22
3
50
4
31
5
32
6
7
8
9
TRAN
X000
TRAN
X002
TRAN
X010
TRAN
X012
41
42
TRAN
X020
TRAN
X022
10
+
M
+
Small Large
X004
LS4
X005
LS5
X001
LS1 Left limit switch
X003
LS3 Upper
limit switch
Origin
indication
Y007
Moving
rightward:
Y003
Moving
leftward:
Y004
Moving up:
Y002
Moving down:
Y000
CY1
X002
LS2 Lower limit switch
When a large ball is pushed, the piston does
not reach the lower limit and X002 does not
turn ON.
Proximity
switch
PS0
X000
Electromagnet
Y001
X026
Start