333
FX3G/FX3U/FX3UC Series Programmable Controllers
Programming Manual - Basic & Applied Instruction Edition
12 Data Operation – FNC 40 to FNC 49
12.10 FNC 49 – FLT / Conversion to Floating Point
11
FNC30-FNC39
Rotation and
Shift
12
FNC40-FNC49
Data Operation
13
FNC50-FNC59
High Speed
Processing
14
FMC60-FNC69
Handy
Instruction
15
FNC70-FNC79
External FX I/O
Device
16
FNC80-FNC89
External FX
Device
17
FNC100-FNC109
Data
Transfer 2
18
FNC110-FNC139
Floating Point
19
FNC140-FNC149
Data
Operation 2
20
FNC150-FNC159
Positioning
Control
12.10 FNC 49 – FLT / Conversion to Floating Point
Outline
This instruction converts a binary integer into a binary floating point (real number).
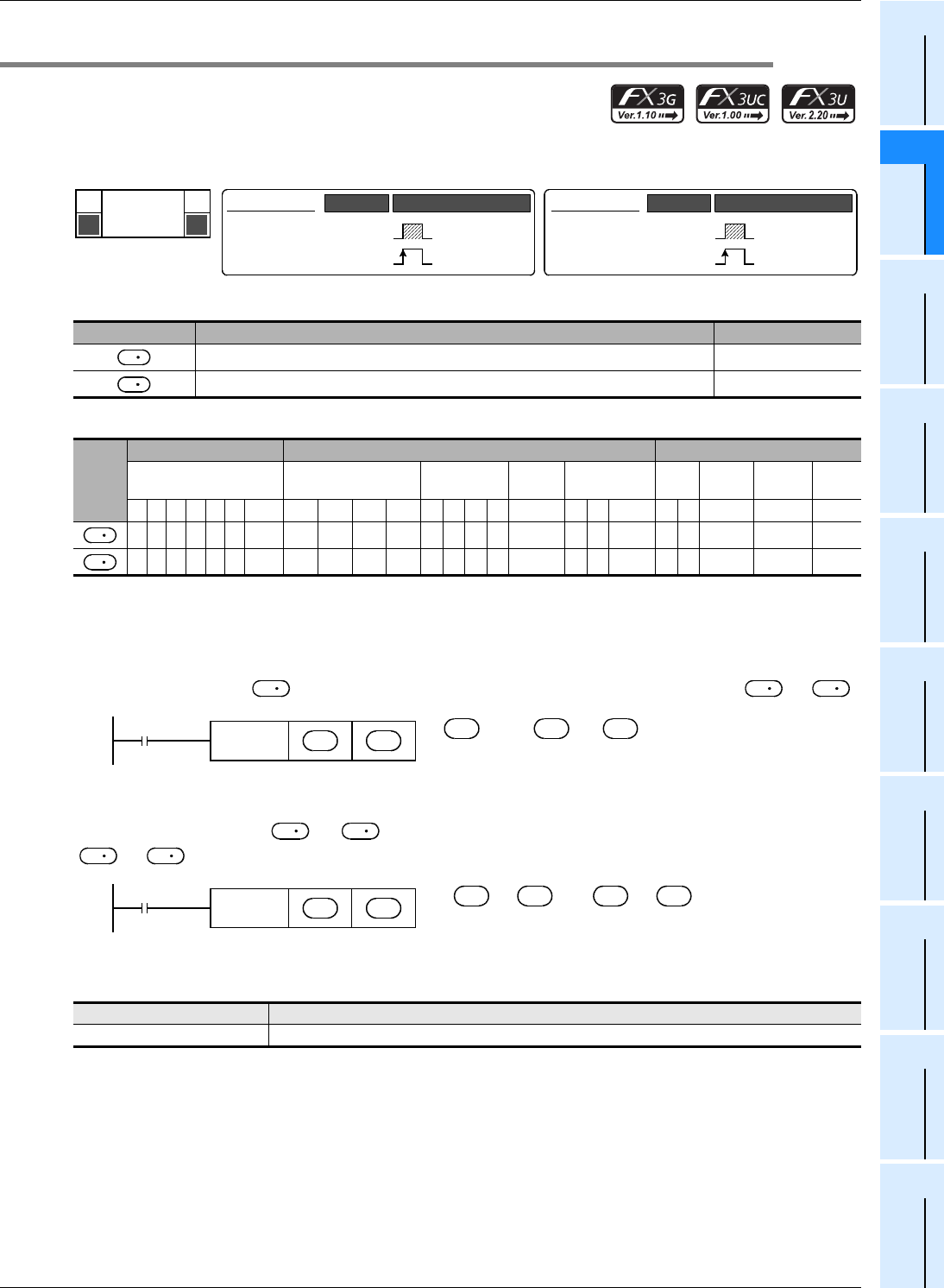
1. Instruction format
2. Set data
3. Applicable devices
S: This function is supported only in FX3U/FX3UC PLCs.
Explanation of function and operation
1. 16-bit operation (FLT and FLTP)
The binary integer data of is converted into binary floating point (real number), and stored to [ +1, ].
2. 32-bit operation (DFLT and DFLTP)
The binary integer data of [ +1, ] is converted into binary floating point (real number), and stored to
[+1, ].
Related instruction
Caution
1. It is not necessary to convert a constant (K or H) into floating point value.
The value of a K or H specified in each instruction for binary floating point (real number) operation is automatically
converted into binary floating point (real number). It is not necessary to convert such a constant using by FLT
instruction.
(K and H cannot be specified in RAD, DEG, EXP and LOGE instructions.)
Operand type Description Data type
Data register number storing binary integer 16- or 32-bit binary
Data register number storing binary floating point (real number) Real number (binary)
Oper-
and
Type
Bit Devices Word Devices Others
System User Digit Specification System User
Special
Unit
Index
Con-
stant
Real
Number
Charac-
ter String
Pointer
XYMTCSD.b KnX KnY KnM KnS T C D R U\G VZModifyKH E ""P
33 S 3
33 S 3
Instruction Description
INT(FNC129) It is inverse of FLT instruction, and converts binary floating point into binary integer.
DFLT
DFLTP
Mnemonic Operation Condition
P
FNC 49
FLT
D
16-bit Instruction
5 steps
FLT
FLTP
Mnemonic Operation Condition
Continuous
Operation
Pulse (Single)
Operation
32-bit Instruction
9 steps
Continuous
Operation
Pulse (Single)
Operation
S
1
S
D
S
1
S
D
D
1
S
D
1
D
D
1
D
Command
input
→
( + 1, )
FNC 49
FLT
S
D
S
D
Binary
integer
D
Binary floating point
(real number)
D
1
S
D
1
S
D
1
D
D
1
D
Command
input
FNC 49
DFLT
S
D
( + 1, )
→
( +1, )
S
S
D
D
Binary integer Binary floating point
(real number)