6 - 31
6 INSPECTION AND MAINTENANCE
6.6.4 Internal I/O circuit troubleshooting
This section describes possible problems with internal I/O circuits and their corrective
actions.
(1) Internal input circuit troubleshooting
The following describes possible problems with internal input circuits and their
corrective actions.
Internal Input Circuit Troubleshooting and Corrective Action
Condition Cause Corrective action
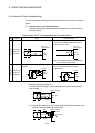
Example 1
Internal input
signal is not
turned OFF.
• Drive by switch with LED indicator.
Motion
controller
Leakage
current
DC input
(plus common)
• Connect an appropriate resistor so that the
current across the Motion controller becomes
lower than the off current.
R
Motion
controller
DC input
(plus common)
Resistor
(Note): A calculation example of the resistance to
be connected is shown below.
Example 2
Internal input
signal is not
turned OFF.
• Sneak path due to the use of two power
supplies.
E1
L
Motion
controlle
r
E1>E2
DC input
E2
• Use only one power supply.
• Connect a sneak path prevention diode.
(Figure below)
E1
L
Motion
controlle
r
DC input
E2
<Calculation example of Example 1>
If a switch with LED display is connected to Motion controller, and current of 4
[mA] is leaked.
Leakage
current 4[mA]
Motion controlle
r
Input signal
part
24VDC
3.6k[ ]
(a) Because the condition for OFF voltage (0.9[mA]) of Motion controller is not
satisfied. Connect a resistor as shown below.
Iz=3.1[mA]
Motion controller
24VDC
4[mA]
RZ
3.6k[ ]
Input impedance
5.6k[ ]
Iz=0.9[mA]