5. Explanation of Devices
- 21 -
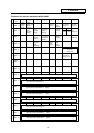
5.3.7 File Register R
(1) As with the data registers, the file registers are memories used to store data. However, there are
some that have fixed applications, and those that are released.
(2) The file register has a 1-point 16-bit configuration, and can be read and written in 16-bit units.
To handle 32-bit data, two points must be used. The file register No. designated with the 32-bit
command will be the low-order 16-bit, and the designated file register No. +1 will be the
high-order 16-bit.
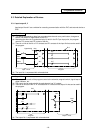
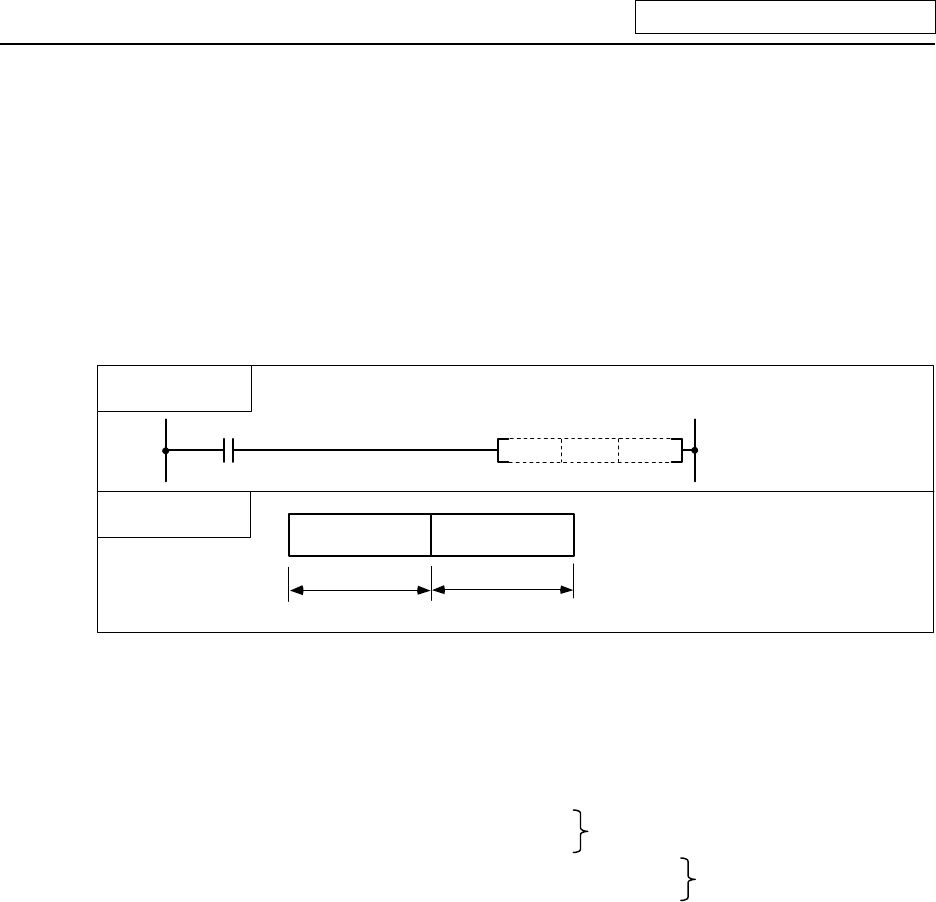
(Example) Use of the DMOV command is shown below.
Low-order 16-bit
Circuit example
Data storage
The X0 to 1F data is
stored in R0,1.
R1
R0
Higth-order 16-bit
(X1F~X10)
(XF~X0)
0
DMOV K8X0
R0
(3) The data that is stored once in the sequence program is held until other data is stored.
(4) With the file registers, the following registers are the user release.
R500 to R549, R1900 to R2799
The following registers of the registers above are not cleared when the power is turned OFF.
R1900 to R2799
The other file registers have fixed applications such as interface of the PLC and CNC, parameter
interface, etc.
(5) Values that can be stored: Decimal -32768 to 32767 For 16-bit command
Hexadecimal 0 to FFFF
(Using Dn)
Decimal -2147483648 to 2147483647 For 32-bit command
Hexadecimal 0 to FFFFFFFF
(Using Dn+1, Dn)