9. Exclusive Commands
- 191 -
9.1 ATC Exclusive Command
9.1.1 Outline of ATC Control
The ATC (Automatic Tool Change) can be controlled in the following two ways:
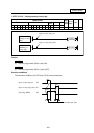
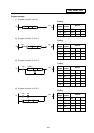
(1) Mechanical random control
With the information of magazine position from the machine, and T command, the control system
determines the direction of magazine rotation, number of steps required, etc. for index of the
magazine, according to the given command.
Each tool and magazine tool pot (socket) have a one-on-one corresponding relation.
Usually, the "intermediate pot" that supports the transfer of the tool is provided between the
spindle and the magazine.
This control is possible by not using ATC command, but ROT command only.
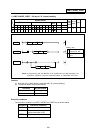
(2) Memory random control
With the information of magazine rotation, or magazine position from the machine, the control
system refers to tool No. stored in the memory. For index of the magazine, the direction of
magazine rotation and number of steps are determined by the given T command and tool No.
stored in the memory.
Each tool and magazine tool pot (socket) does not always have a one-on-one corresponding
relation.
Usually, the "intermediate pot" is not provided.
9.1.2 ATC Operation
The motions related to ATC operation can be largely divided into the following four motions:
(1) Index of magazine ……………………...………. (ATC-K1, K2, K5, K6, K7, K8)
(2) Tool change (arm, or the like is used) ……...... (ATC-K3, K4)
(3) Transfer of tool to intermediate pot or arm ..... (Normal function commands such as MOV, XCH
are used.)
(4) Others ..………………………………………….. (ATC-K9, K10, K11)
9.1.3 Explanation of Terminology
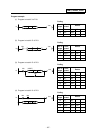
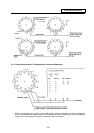
(1) Pointer
This points out the position where the magazine is indexed. When a tool table in which tool No.
are previously recorded is used, the tool table does not rotate with rotation of the magazine and
the pointer serves as "ring counter" for control of magazine position.
(2) Fixed pointer
This is the type with tool pots numbered and the relationship between tool pot and tool No. is
fixed if the magazine is rotated. When the tool table is rotated, fixed pointer does not functionally
differ from "floating pointer".
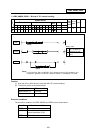
(3) Floating pointer
This is the type with numbered fixed position on magazine and the relationship between
magazine No. and tool No. changes when the magazine rotates.