70
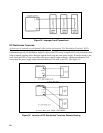
connection to ground or chassis--or when there are multiple loads and only one has an internal connection to
ground or chassis (Figure 43).
Figure 43. Ground Connections for Multiple Loads, One Grounded
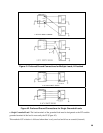
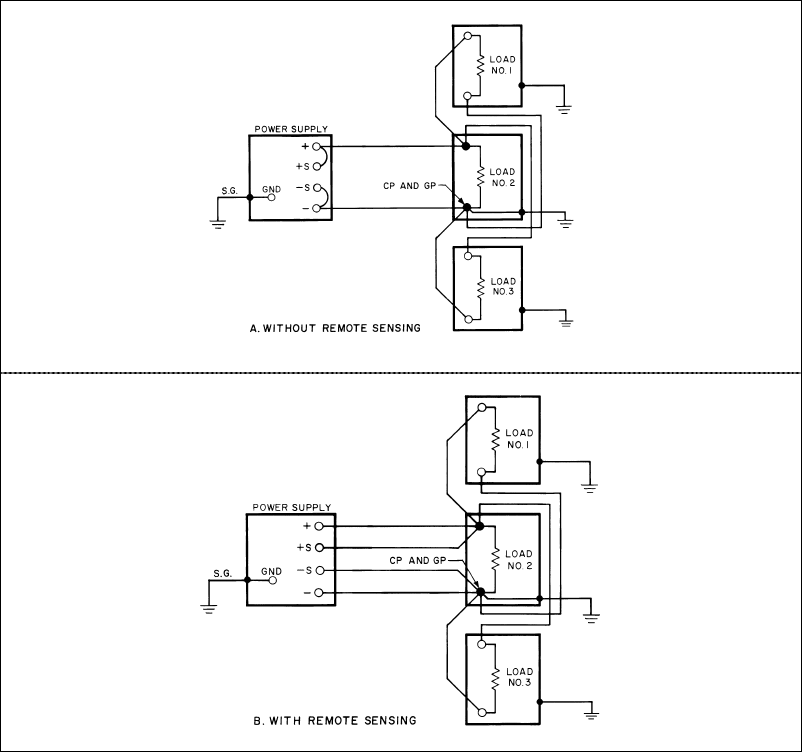
d. Multiple Loads, Two or More of Which are Individually Grounded--This is an undesirable situation and
must be eliminated if at all possible. Ground loop currents circulating through the dc and load wiring cannot be
avoided as long as separate loads connected to the same power supply (or dc system) have separate ground
returns (Figure 44).
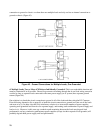
One solution is to break the circuit connection to ground in all of the loads and then select the DC Common
Point following alternative (b) on page 68, or break the circuit connection to ground in all but one of the loads
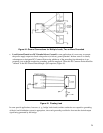
and treat as in (c). In other cases the only satisfactory solution is to increase the number of power supplies,
operating each grounded load from its own separate supply, and treating each combination of power supply and
load as in (c). However, in this case any conductive path remaining between the loads may degrade load
performance, and any conductive path between power supplies (except via their respective load grounds) will
probably degrade both power supply and load performance.