66
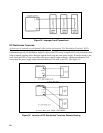
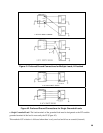
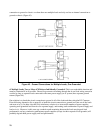
Figure 38. Local Decoupling Capacitors
The ideal concept of a single "quiet" ground potential is a snare and a delusion. No two ground points have
exactly the same potential. The potential differences in many cases are small, but even a difference of a fraction
of a volt in two ground potentials will cause amperes of current to flow through a complete ground loop (any
circuit with more than one ground point).
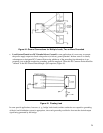
To avoid ground loop problems, there must be only one ground return point in a power supply system (the
power supply and all its loads, and all other power supplies connected to the same loads). However, the
selection of the best DC Ground Point is dependent upon the nature and complexity of the load and the dc
wiring, and there are practical problems in large systems which tend to force compromises with the ideal
grounding concept.
For example, a rack mounted system consisting of separately mounted power supplies and loads generally has
multiple ground connections -- each instrument usually has its own chassis tied to the third "Safety Ground"
lead of its power cord, and the rack is often connected by a separate wire to "Safety Ground" (the cold water
pipe). With the instrument panels fastened to the rack frame, circulating ground currents are inevitable.
However, as long as these ground currents are confined to the "Ground System" and do not flow through any
portion of the power supply dc distribution wiring, the effect on system performance is probably negligible. To