50
output terminal and the guard has no effect on the output impedance. The meter still measures the output
voltage because the guard is at the same potential as the positive output terminal. The front-panel voltmeter is
internally connected to guard; and if greater accuracy is needed, a voltmeter can be connected externally.
Unlike other guards, such as those used on digital voltmeters, the guard in the Current Source is active and
internally referenced to the positive terminal. For this reason the guard is labeled "(+) meter" on the front panel.
and must not be connected to either output terminal, since this interferes with the closed loop performance.
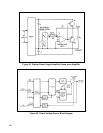
Transformer Shielding Eliminates Ripple. Agilent Current Sources meet their low ripple specifications
regardless of which output terminal, if either, is connected to earth ground. High-gain current regulation is one
reason for the low ripple. Another is special shielding to keep ac voltages in the power transformer from being
coupled into the output via the capacitance between the transformer windings and the output or ground.
One potential source of ripple current is capacitive coupling between the primary winding and the negative
output terminal. This problem is eliminated by enclosing the primary winding in an electrostatic shield which is
connected to earth ground. A second source of ripple current is capacitive coupling between the secondary
winding and ground. To keep this current from affecting the output, the secondary winding is enclosed in an
electrostatic shield which is connected to the negative output terminal. This causes the ripple current generated
by the secondary winding to be confined to a closed loop inside the instrument.
Extended Range Power Supplies
This type of supply automatically extends the number of output voltage and current combinations that are
available within the maximum power rating of a single unit. Before discussing circuit techniques, the following
paragraphs first outline the advantages of the extended range concept itself.
Advantages of Extended Range
Figure 28 compares the output characteristic of a conventional CV/CC supply with that of an extended range
supply of the same output power (200W in the example). As indicated in 28(A) maximum output power from a
conventional supply can be obtained at only one point (20V/10A) on its rectangularly shaped locus. Maximum
output power for an extended range supply, however, is available not only at 20V/10A, but at 50V/4A and
anywhere along the curved portion of the characteristic ranging between 20 and 50V.
To duplicate this capability would require either one large 500W power supply operating inefficiently at less
than rated output at many operating points, or else several equivalent supplies; a 50V/4A supply, a 20V/10A
supply, and others for in-between voltage and current ratings. Both of these solutions are expensive and require
a significant amount of bench or rack space.