148
7-1 Introduction
This section provides the procedures for inputting and debugging a program
and monitoring and controlling the PC through a Programming Console. The
Programming Console is the most commonly used Programming Device for
the K-type PCs. It is compact and available both in hand-held models or
CPU-mounted models. Refer to
Appendix A Standard Models
for model num-
bers and other details.
If you are using a GPC, FIT, or a computer running LSS, refer to the
Opera-
tion Manual
for corresponding procedures on these. If you are going to use a
GPC, FIT, or a computer running LSS, but want to input in mnemonic code
rather than in ladder diagram form, refer to
4-3-2 Mnemonic Code
.
7-2 Debugging
After inputting a program and correcting it for syntax errors, it must be exe-
cuted and all execution errors must be eliminated. Execution errors include
an excessively long cycle time, errors in settings for various Units in the PC,
and inappropriate control actions, i.e., the program not doing what it is de-
signed to do.
When necessary, the program can first be executed isolated from the actual
control system and wired to artificial inputs and outputs to check for certain
types of errors before actual trial operation with the controlled system.
When an error occurs during program execution, it can be displayed for iden-
tification by pressing CLR, FUN, and then MONTR. If an error message is
displayed, the MONTR key can be press to access any other error messages
that are stored by the system in memory. If MONTR is pressed in PROGRAM
mode, the error message will be cleared from memory; be sure to write down
the error message when required before pressing MONTR. OK will be dis-
played when the last message has been cleared.
If a beeper sounds and the error cannot be cleared by pressing MONTR, the
cause of the error still exists and must be eliminated before the error mes-
sage can be cleared. If this happens, take the appropriate corrective action to
eliminate the error. Refer to
Section 8 Troubleshooting
for all details on all
error messages. The sequence in which error messages are displayed de-
pends on the priority levels of the errors. The messages for fatal errors (i.e.,
those that stop PC operation) are displayed before non-fatal ones.
Although error messages can be displayed in any mode, they can be cleared
only in PROGRAM mode. There is no way to restart the PC following a fatal
error without first clearing the error message in PROGRAM mode.
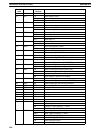
Displaying and Clearing
Error Messages
Key Sequence
Debugging Section 7-2