Software Developer’s Manual 149
Power Management
6.4.3.3 Flexible Filter
The Ethernet controller supports a total of four flexible filters. Each filter is configured to
recognize any arbitrary pattern within the first 128 bytes of the packet. To configure the flexible
filter, the software driver must mask values into the Flexible Filter Mask Table (FFMT), the
required values into the Flexible Filter Value Table (FFVT), and the minimum packet length into
the Flexible Filter Length Table (FFLT). These contain separate values for each filter. The software
driver must also enable the filter in the Wakeup Filter Control Register (WUFC) as well as the
overall wakeup functionality by setting
PME_En in the Power Management Control Status
Register or the Wakeup Control Register.
Once enabled, the flexible filters scan incoming packets for a match. If the filter encounters any
byte in the packet where the mask bit is 1b and the byte doesn’t match the byte programmed in the
Flexible Filter Value Table (FFVT), then the filter failed that packet. If the filter reaches the
required length without failing the packet, it passes the packet and generates a wakeup event. It
ignores any mask bits set to 1b beyond the required length. (the wakeup packet is stored, see
Section 6.4.3.5).
For the
82541xx and 82547GI/EI, the flexible filter does not have any way to automatically skip
VLAN or LLC/SNAP headers. If such headers are included, the offsets of the subsequent fields
must be adjusted accordingly.
Note: This following flexible packet filters are listed for reference only.
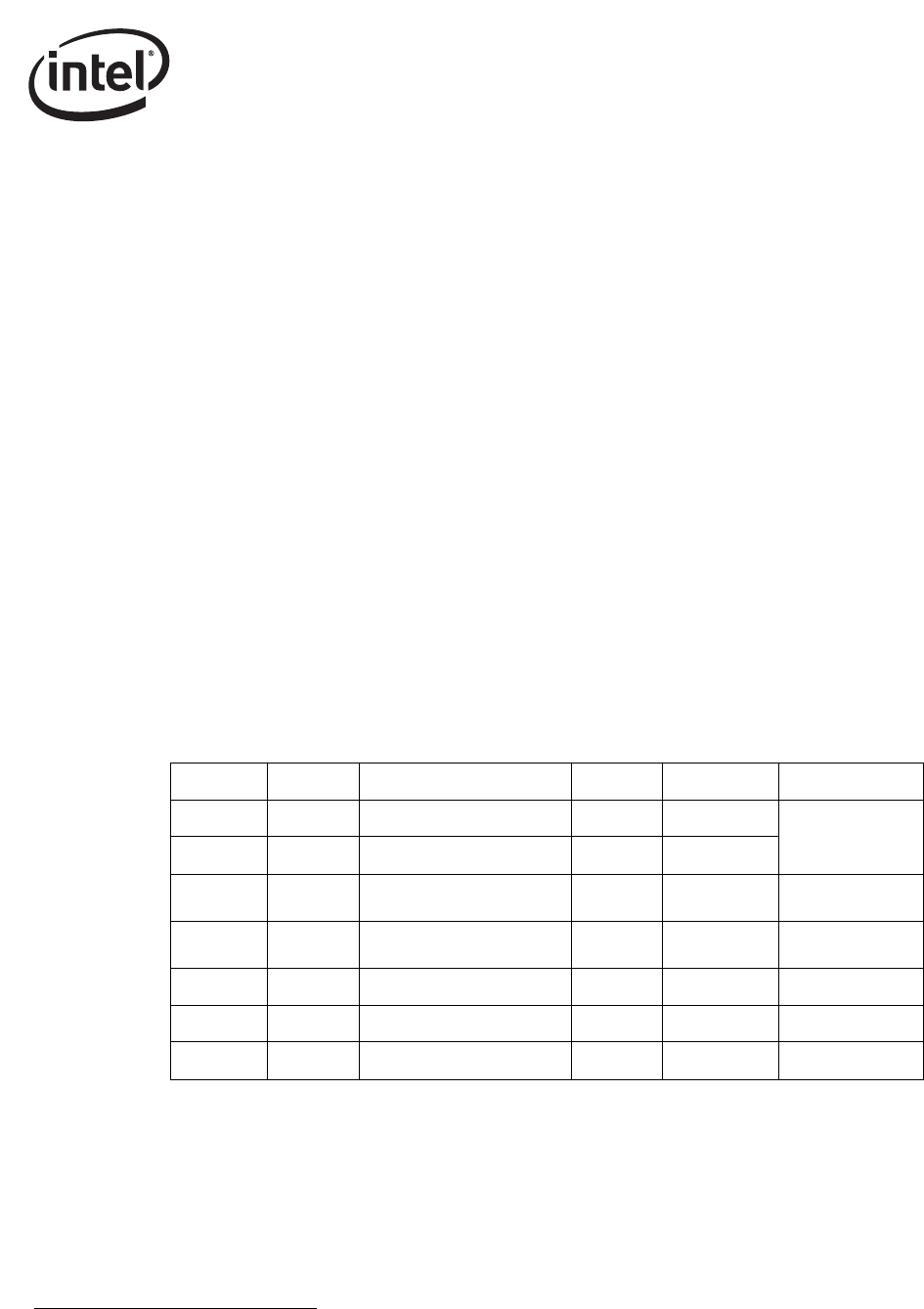
6.4.3.3.1 IPX Diagnostic Responder Request Packet Example
1
1. 82541xx and 82547GI/EI only.
Offset # of bytes Field Value Action Comment
0 6 Destination Address Compare
MAC Header –
processed by
main address filter
6 6 Source Address Skip
12 S = (0/4) Possible VLAN Tag
Compare or
Skip
12 + S D = (0/8) Possible LLC/SNAP Header
Compare or
Skip
12 + D + S 2 Type 8137h Compare IPX
14 + D + S 16 Some IPX Stuff - Ignore
30 + D + S 2 IPX Diagnostic Socket 0456h Compare


















