Intel
®
855GME and Intel
®
852GME Thermal Design Guide for Embedded Applications 31
Thermal Management Features and Tools
7.5.2 Temperature Triggered Throttling
Temperature triggered throttling will limit the maximum achievable bandwidth as a safeguard
against a thermal virus only when the junction temperature reaches a specified trip point
temperature. This method of thermal throttling is an improvement over the bandwidth
triggered throttling method because the chipset MCH will only reduce bandwidth
performance when it is absolutely necessary under a preset condition.
The temperature throttle trip point is programmed into the chipset MCH at boot. If the temperature
of the chipset MCH goes beyond the trip point limit, the chipset MCH will be throttled to a
predetermined maximum throttling amount until the temperature drops below the same
temperature limit.
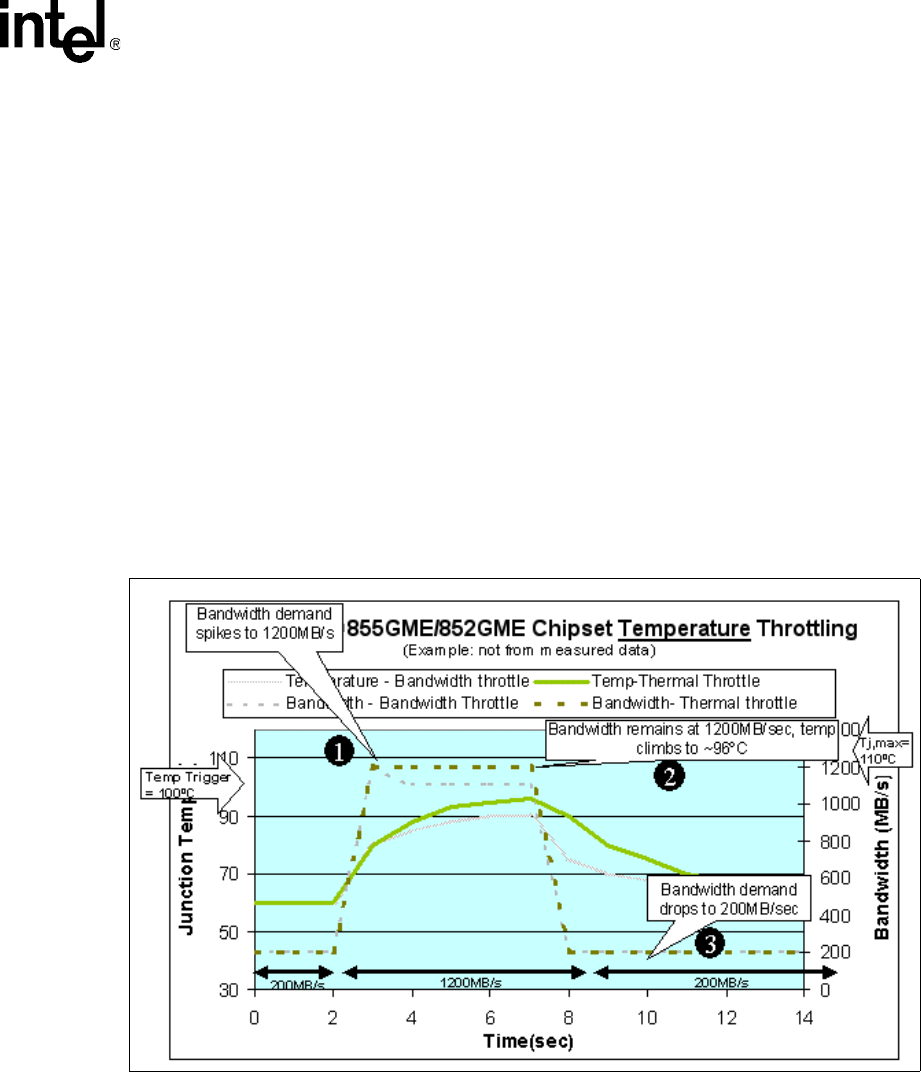
Figure 20 below provides an example of how temperature triggered throttling would optimize
throttling under conditions similar to the scenario that was described in Section 7.5.1. In this
scenario the hot trip temperature is set at 100 ºC. Keep in mind that the Tj,max specification for the
855GME and 852GME chipset MCHs is 110 ºC and the example described in the section is only
intended to illustrate the behavior. The hot trip temperature represents the temperature setpoint at
which the chipset MCH will initiate throttling.
1. The system is operating at an idle workload until an application that requires a large amount of
bandwidth is initiated. The application demands a peak bandwidth of 1200 MB/sec. and the
chipset MCH will sustain this bandwidth level until the temperature climbs above the hot trip
setting of 100 ºC.
2. During this test the chipset MCH operates at a 1200 MB/sec. bandwidth level for a period
longer than the sampling window because the junction temperature has not increased above
the hot trip point setting. In this case the chipset MCH is demonstrating better bandwidth
performance while operating under the same application as in the bandwidth triggering case.
This is clearly a preferred method of throttling the chipset MCH only when it is absolutely
necessary.
Figure 20. 855GME/852GME chipset MCH Temperature Throttling


















