Page 108
7.3 Index Modification
When registers are used as operands of instructions, the method of directly designating the register address as
shown in Example 1) below is called ‘direct addressing’.
As opposed to this, the method of indirectly designating the register by combination with the contents of the index
register (I, J, or K) as shown in Example 2 below is called ‘indirect addressing’. In particular, in this case, since the
address is modified using an index register, this is called ‘index modification’.
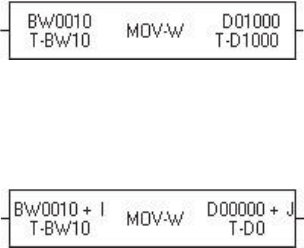
Example - 1)
Data transfer instruction
Transfer data of BW010 to D1000
Example - 2)
Data transfer instruction (with index modification)
Transfer data of BW(10 + I) to D(0000 + J)
(If I = 3 and J = 200, the data of BW13 is transferred to D0200).
There are 3 types of index registers, I, J and K. Each type processes 16-bit integers (-32768 to 32767). There are
no particular differences in function between these 3 types of index registers.
There is no special instruction for substituting values in these index registers. These are designated as destination of
data transfer instructions, etc.