Appendix - 80
MELSEC-Q
APPENDICES
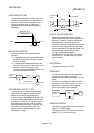
LINEAR INTERPOLATION
This automatic operation simultaneously
operates two motors for the latitudinal (X) feed
and longitudinal (Y) feed to move a target in a
diagonal line for positioning. Three or four
motors can also be operated simultaneously.
The QD75 combines the operation of axis 1
through 4 for the linear interpolation. The same
positioning data No. must be used for the
setting. Refer to the term "INTERPOLATION
OPERATION".
No.9
No.8
No.1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Longitudinal
feed
Latitudinal feed
LOAD INERTIA RATIO
GDL
2
/GDM
2
Refer to "GD
2
".
LOW-INERTIA MOTOR
This is a motor used when frequent
acceleration/deceleration is repeated. Low-
inertia motors are longitudinally longer, to
decrease the rotor diameter and cover the
torque. This enables their inertia moment to be
reduced up to 1/3 that of standard motors. The
ideal load inertia ratio is 1 or less.
M CODE (Machine Code)
These are sub functions that interlock with the
positioning operation to replace drills, tighten
and loosen clamps, raise and lower welding
electrodes, display various data, etc.
Either of two modes can be entered when the
machine code turns ON: AFTER or WITH.
The machine does not move to the next
positioning when the machine code is ON. M
codes are turned OFF by the PLC program.
Code Nos. from 1 to 65535 assigned by the
user and used (1: Clamp, 2: Loosen, etc.).
Comments can be written after 50 of the M
codes, and they can be monitored using a
peripheral device or displayed on an external
display. Refer to "AFTER MODE" and "WITH
MODE".
MACHINE FEED VALUE
The OP address at the completion of the
machine OPR is stored.
The current position of the machine
coordinates determined by a machine having
the OP address as a reference.
Even if the current value is changed, this value
will not change.
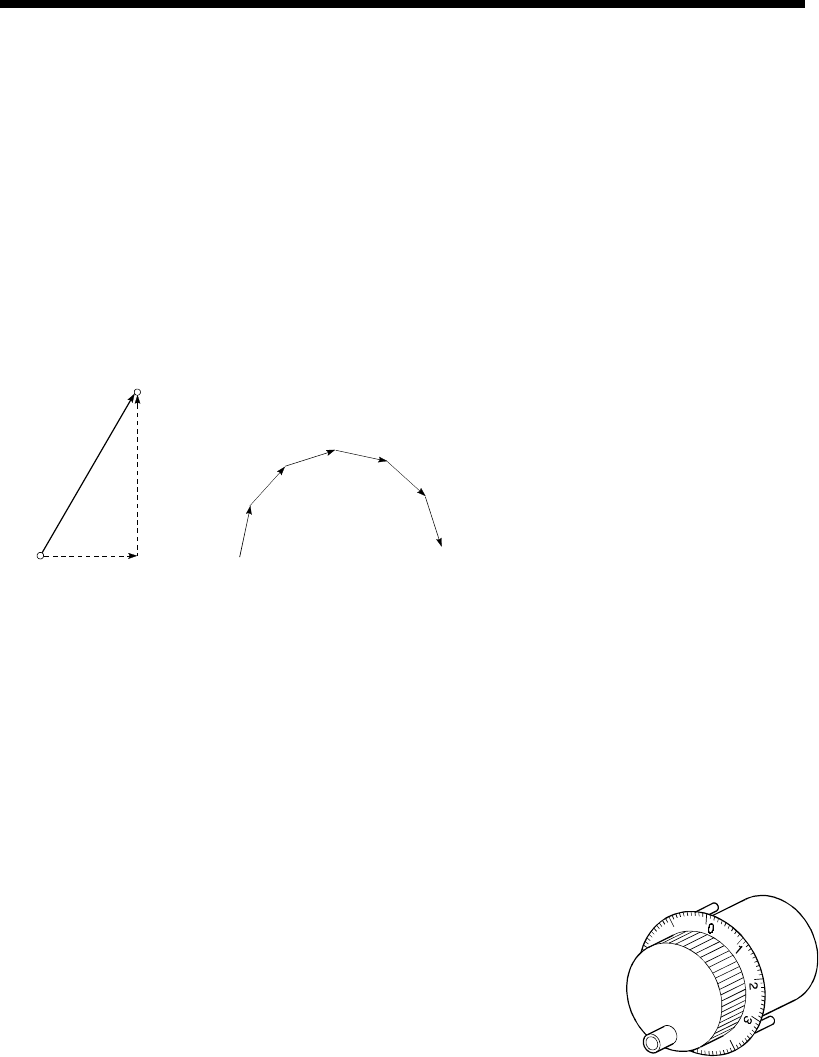
MANUAL PULSE GENERATOR
The handle of this device is manually rotated
to generate pulses. This device is used when
manually carrying out accurate positioning.
Made by Mitsubishi Electric Corp.
(model: MR-HDP01)
MASTER AXIS
When carrying out interpolation operations,
this is the side on which the positioning data is
executed in priority. For example, when
positioning with the X axis and Y axis, the side
with the largest movement distance will
become the master axis, and the speed will
follow that axis. The slave axis speed will be
ignored.