3 - 6
MELSEC-Q
3 SPECIFICATIONS AND FUNCTIONS
3.2.2 QD75 main functions
The outline of the main functions for positioning control with the QD75 is described
below. (Refer to Section 2 for details on each function.)
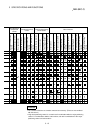
Main functions Details
Reference
section
Machine OPR control
Mechanically establishes the positioning start point using
a near-point dog or stopper. (Positioning start No. 9001)
8.2
OPR control
Fast OPR control
Positions a target to the OP address (
Md.21
Machine
feed value) stored in the QD75 using machine OPR.
(Positioning start No. 9002)
8.3
Linear control
(1-axis linear control)
(2-axis linear interpolation control)
(3-axis linear interpolation control)
(4-axis linear interpolation control)
Positions a target using a linear path to the address set in
the positioning data or to the position designated with the
movement amount.
9.2.2
9.2.3
9.2.4
9.2.5
Fixed-feed control
(1-axis fixed-feed control)
(2-axis fixed-feed control)
(3-axis fixed-feed control)
(4-axis fixed-feed control)
Positions a target by the movement amount designated
with the amount set in the positioning data.
(With fixed-feed control, the "
Md.20
Current feed value"
is set to "0" when the control is started. With
2-, 3-, or 4-axis fixed-feed control, the fixed-feed is fed
along a linear path obtained by interpolation.)
9.2.6
9.2.7
9.2.8
9.2.9
Position
control
2-axis circular interpolation control
Positions a target using an arc path to the address set in
the positioning data, or to the position designated with the
movement amount, sub point or center point.
9.2.10
9.2.11
Speed
control
Linear control
(1-axis linear control)
(2-axis linear interpolation control)
(3-axis linear interpolation control)
(4-axis linear interpolation control)
Continuously outputs the pulses corresponding to the
command speed set in the positioning data.
9.2.12
9.2.13
9.2.14
9.2.15
Speed-position switching control
First, carries out speed control, and then carries out
position control (positioning with designated address or
movement amount) by turning the "speed-position
switching signal" ON.
9.2.16
9.2.17
Position-speed switching control
First, carries out position control, and then carries out
speed control (continuous output of the pulses
corresponding to the designated command speed) by
turning the "position-speed switching signal" ON.
9.2.18
Current value changing
Changes the Current feed value (
Md.20
) to the address
set in the positioning data.
The following two methods can be used.
(The machine feed value cannot be changed.)
• Current value changing using positioning data
• Current value changing using current value changing
start No. (No. 9003)
9.2.19
NOP instruction
No execution control system. When NOP instruction is
set, this instruction is not executed and the operation of
the next data is started.
9.2.20
JUMP instruction
Unconditionally or conditionally jumps to designated
positioning data No.
9.2.21
LOOP Carries out loop control with repeated LOOP to LEND. 9.2.22
Major positioning control
Other
control
LEND
Returns to the beginning of the loop control with repeated
LOOP to LEND.
9.2.23