4-7
Integrated Services Adapter and Integrated Services Module Installation and Configuration
OL-3575-01 B0
Chapter 4 Configuring the ISA and ISM
Creating Crypto Maps
Table 4-1 shows allowed transform combinations.
Creating Crypto Maps
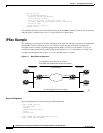
Crypto map entries created for IPSec pull together the various elements used to set up IPSec security
associations, including:
• Which traffic should be protected by IPSec (according to a crypto access list)
• Granularity of the flow to be protected by a set of security associations
• Where IPSec-protected traffic should be sent (who the remote IPSec peer is)
• Local address to be used for the IPSec traffic (see the “Applying Crypto Maps to Interfaces” section
on page 4-9 for more details)
• What IPSec security should be applied to this traffic (selecting from a list of one or more transform
sets)
• Whether security associations are manually established or are established through IKE
• Other parameters that might be necessary to define an IPSec security association
Crypto map entries with the same crypto map name (but different map sequence numbers) are grouped
into a crypto map set. Later, you will apply these crypto map sets to interfaces; then, all IP traffic passing
through the interface is evaluated against the applied crypto map set. If a crypto map entry sees outbound
IP traffic that should be protected and the crypto map specifies the use of IKE, a security association is
negotiated with the remote peer according to the parameters included in the crypto map entry; otherwise,
if the crypto map entry specifies the use of manual security associations, a security association should
have already been established through configuration.
(If a dynamic crypto map entry sees outbound traffic that should be protected and no security association
exists, the packet is dropped.)
The policy described in the crypto map entries is used during the negotiation of security associations. If
the local router initiates the negotiation, it uses the policy specified in the static crypto map entries to
create the offer to be sent to the specified IPSec peer. If the IPSec peer initiates the negotiation, the local
router checks the policy from the static crypto map entries, as well as any referenced dynamic crypto
map entries, to decide whether to accept or reject the peer’s request (offer).
Table 4-1 Allowed Transform Combinations
AH Transform
1
1. Pick one transform option.
ESP Encryption Transform
1
ESP Authentication Transform
2
2. Pick one transform option, but only if you selected esp-null or ESP encryption transform.
Transform Description Transform Description Transform Description
ah-md5-hma
c
AH with MD5
(HMAC variant)
authentication
algorithm
esp-3des ESP with 168-bit Triple
DES encryption algorithm
esp-md5-hma
c
ESP with MD5
(HMAC variant)
authentication
algorithm
ah-sha-hmac AH with SHA
(HMAC variant)
authentication
algorithm
esp-des ESP with 56-bit DES
encryption algorithm
esp-sha-hmac ESP with SHA
(HMAC variant)
authentication
algorithm
esp-null ESP transform without
cipher