3. Input/Output Signals
- 5 -
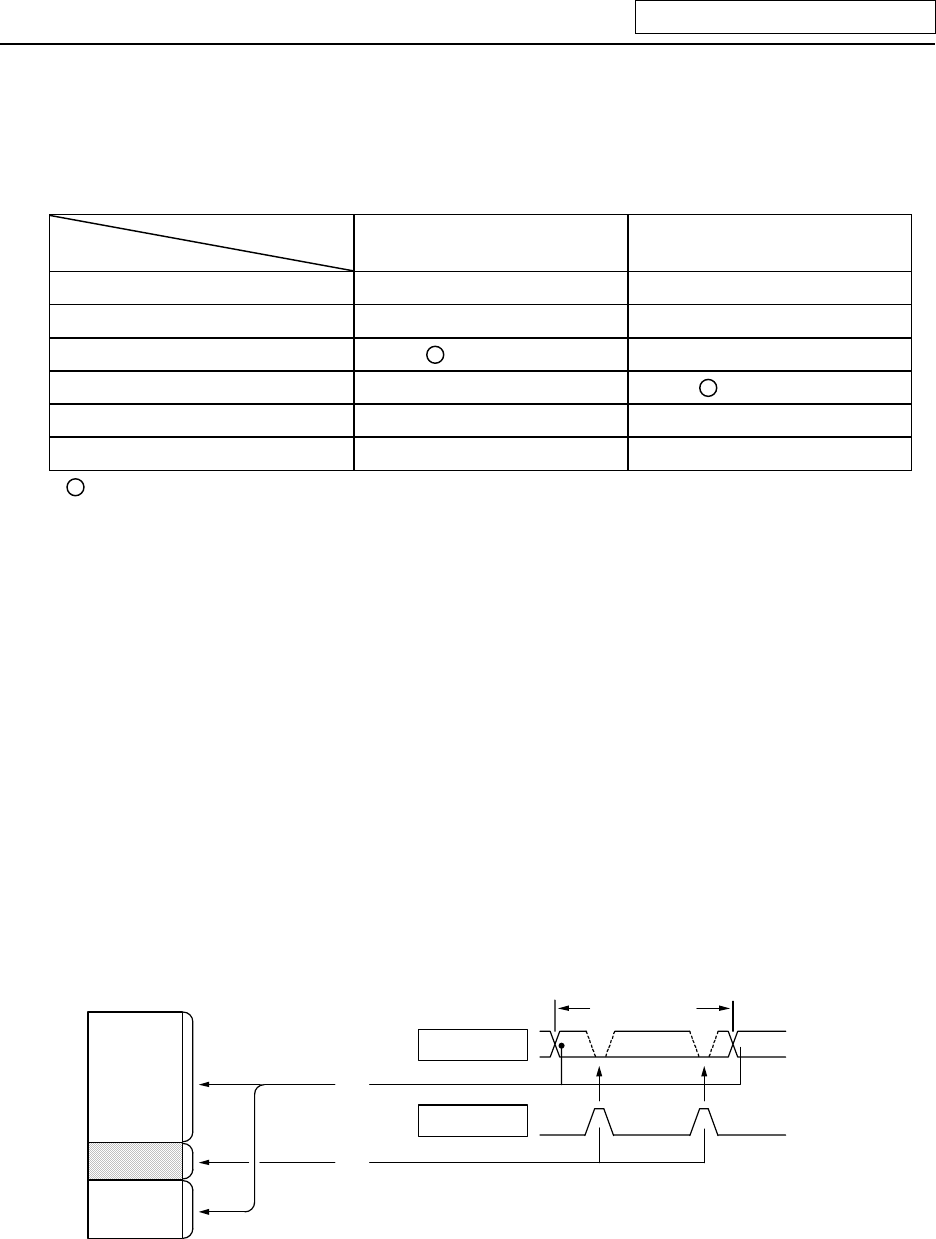
Table 3.1-1 lists whether or not high-speed input/output, interrupt input and initial processing can be
performed.
Table 3.1-1 Whether or not high-speed input/output, interrupt input and initial
can be performed
High-speed input
specification
High-speed output
specification
Input signal from control unit
x x
Output signal to control unit
x x
Input signal from machine
(2-byte units) x
Output signal to machine
x
(2-byte units)
Input signal from operation board
x x
Output signal to operation board
x x
: Possible x : Not possible
The operation board in Table 3.1-1 is applied when control is performed by operation board
input/output card that can be added as NC option.
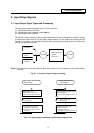
3.2 Handling of Input Signals Designated for High-Speed Input
The input/output signals used in user PLC are input/output for each program level as shown in
Fig. 3.1-2.
In high-speed processing, input/output signal for which high-speed input or output designation
(parameter) is made is input or output each time the high-speed processing program runs. In main
processing, signals other than interrupt input signals or high-speed input/output designation are
input/output.
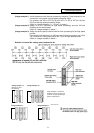
When high-speed input designation signal is used in main processing, the input signal may change
within one scan because high-speed processing whose level is higher than main processing
interrupts. Input signal which must not change within one scan should be saved in temporary memory
(M), etc., at the head of main processing and the temporary memory should be used in the main
program, for example.
High-speed
processing
Main
processing
(2) Set at the head of high-speed processing.
(1) Set at the head of main processing.
A B
Input image memory
PLC one scan
(1)
(2)
A
The hatched area is high-speed input designation part. Whenever the high-speed processing
program runs, data is reset in the hatched area. Thus, the signal in the hatched area may change in
main processing (A) and (B) because the high-speed process interrupts between (A) and (B) and
re-reads the input signal in the hatched area.