6 - Introduction to Programming
66
Data
Ke
y
words
Ke
y
word Se
p
arator
Messa
g
e Unit Se
p
arators
Messa
g
e Unit
Quer
y
Indicator
Messa
g
e Terminator
Root S
p
ecifier
VOLT <NL>
: LEV 20
PROT 21
;
;
: CURR?
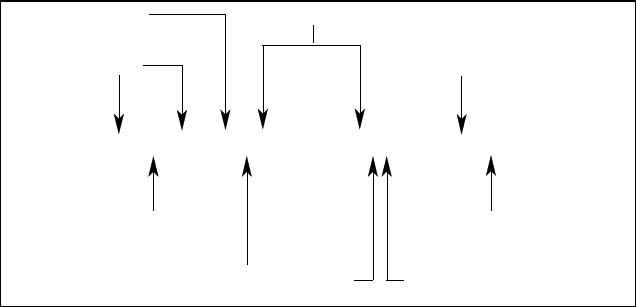
Figure 6-2. Command Message Structure
Headers
Headers, also referred to as keywords, are instructions recognized by the dc source. Headers may be
either in the long form or the short form. In the long form, the header is completely spelled out, such as
VOLTAGE, STATUS, and DELAY. In the short form, the header has only the first three or four letters,
such as VOLT, STAT, and DEL.
Query Indicator
Following a header with a question mark turns it into a query (VOLTage?, VOLTage:PROTection?). If a
query contains a parameter, place the query indicator at the end of the last header.
VOLTage:PROTection? MAX
Message Unit Separator
When two or more message units are combined into a compound message, separate the units with a
semicolon.
STATus:OPERation?;QUEStionable?
Root Specifier
When it precedes the first header of a message unit, the colon becomes the root specifier. It tells the
command parser that this is the root or the top node of the command tree.
Message Terminator
A terminator informs SCPI that it has reached the end of a message. Three permitted messages
terminators are:
♦ newline (<NL>), which is ASCII decimal 10 or hex 0A.
♦ end or identify (<END>)
♦ both of the above (<NL><END>).
In the examples of this guide, there is an assumed message terminator at the end of each message.


















