1-14
LOAD CONSIDERATIONS
This section provides information on operatin
our suppl
with
various t
pes of loads connected to its output.
PULSE LOADING
The power suppl
will automaticall
cross over from constant-
volta
e to constant current operation in response to an increase
(over the preset limit) in the output current. Althou
h the preset
limit ma
be set hi
her than the avera
e output current, hi
h peak
currents (as occur in pulse loadin
) ma
exceed the preset cur-
rent limit and cause cross over to occur. If this cross over limitin
is not desired, set the preset limit for the peak requirement and
not the avera
e.
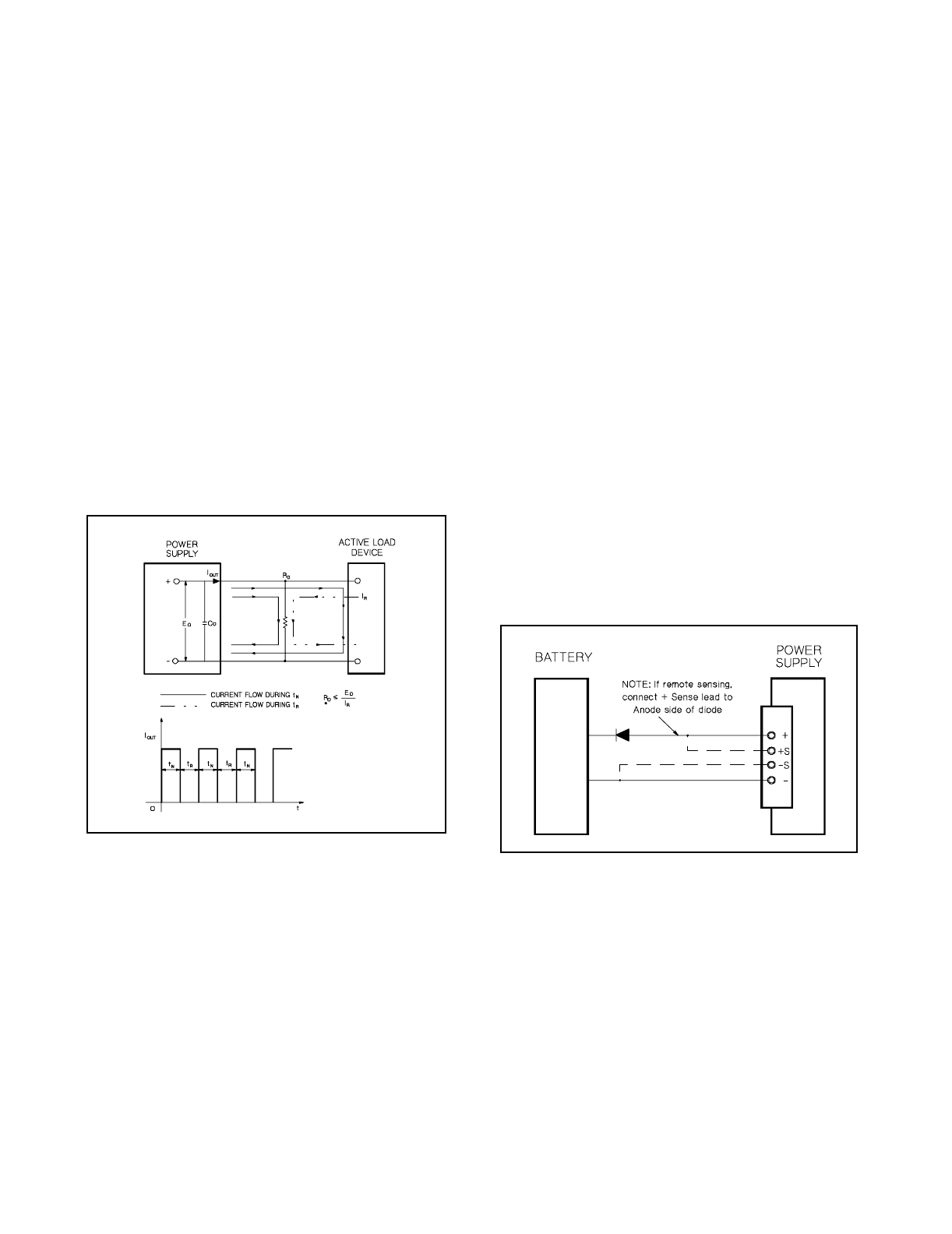
REVERSE CURRENT LOADING
An active load connected to the power suppl
ma
actuall
deliver a reverse current to the power suppl
durin
a portion of
its operatin
c
cle. An external source can not be allowed to
pump current into the suppl
without loss of re
ulation and possi-
ble dama
e to the output capacitor of the power suppl
. To avoid
these effects, it is necessar
to preload the suppl
with a dumm
load resistor so that the power suppl
delivers current throu
h the
entire operatin
c
cle of the load devices.
Fi
ure 16. Reverse Current Loadin
Solution
OUTPUT CAPACITANCE
An internal capacitor, connected across the output terminals of
the power suppl
, helps to suppl
hi
h-current pulses of short
duration durin
constant volta
e operation. An
capacitance
added externall
will improve the pulse current capabilit
, but will
decrease the safet
provided b
the current limitin
circuit. A
hi
h-current pulse ma
dama
e load components before the
avera
e output current is lar
e enou
h to cause the current limit-
in
circuit to operate.
The effect of the output capacitor durin
constant current opera-
tion are as follows:
a. The output impedance of the power suppl
decreases with
increasin
frequenc
.
b. The recover
time of the output volta
e is lon
er for load
resistance chan
es.
c. A lar
e sur
e current causin
a hi
h power dissipation in the
load occurs when the load resistance is reduced rapidl
.
REVERSE VOLTAGE LOADING
A diode is connected across the output terminals with reverse
polarit
. This diode protects the output electrol
tic capacitors and
the series re
ulator transistors from the effects of a reverse volt-
a
e applied across the output terminals. For example, in series
operation of two supplies, if the AC is removed from one suppl
,
the diode prevents dama
e to the unener
ized suppl
which
would otherwise result from a reverse polarit
volta
e.
Since series re
ulator transistors cannot withstand reverse volt-
a
e, another diode is connected across the series transistor. This
diode protects the series re
ulators in parallel or auto-parallel
operation if one suppl
of the parallel combination is turned on
before the other.
BATTERY CHARGING
The power suppl
's OVP circuit contains a crowbar SCR, which
effectivel
shorts the output of the suppl
whenever the OVP trips. If
an external volta
e source such as a batter
is connected across the
output, and OVP inadvertentl
tri
ered, the SCR will continuousl
sink a lar
e current from the source; possibl
dama
in
the suppl
.
To avoid this a diode must be connected in series with the output as
shown in Fi
ure 17.
Fi
ure 17. Recommended Protection Circuit for
Batter
Char
in
